What is Python:
Python is a computer programming language often used to build websites and software, automate tasks, and conduct data analysis. Python is an interpreted, High Level, general-purpose programming language. Python also offers the ability to easily automate processes through scripting, making it key for software testing, troubleshooting and bug tracking.
Advantages of Python:
Presence of a third-party module
Extensive support libraries
open source and community development
learning ease and support available
User-Friendly data structure
Productivity and speed
Applications of Python:
Language development
web framework and web applications
Gui-based desktop applications
Python Practise:
Variables: Variables are the containers where you can store the values in it

Taking Input from the User:

Multi-assigment:

Stroing the string values: we can store the string similarly we store the values of numbers

Lists: A list is a special datatype in python that is mutable or changeable, ordered sequence of elements. Each element or value that is inside of a list is called an item.

Tuple: Tuple is a collection that is ordered and unchangeable. In the Python tuple, you can access it by retrieving the index number.

Sets: A set is a collection that is underaged and unindexed. In Python sets are cannot access by retrieving the index. It is denoted by Curly brackets

Dictionaries: A dictionary is a collection that is unordered, changeable and indexed. It is written in curly brackets and they have the keys and the values.

Important Topic in Python and machine learning is:
The topic is Indexing, Slicing, Fromating, and concatenation:
Indexing: To retrieve an element, we use the index operator.
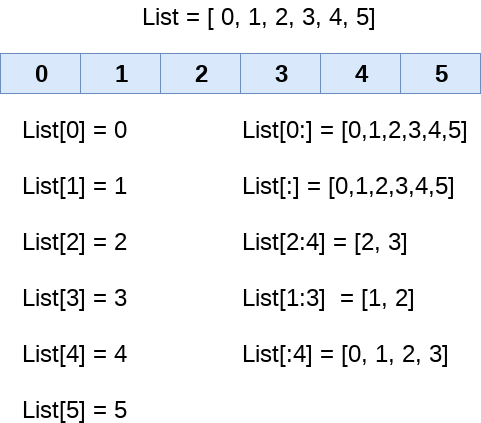
Slicing: Slicing means getting a subset of an element from an iterable based on its indices.

String formatting: Python uses 'c' - style string formatting to create new, formatted strings.

String concatenation: In Python, there are a few ways to concatenate or combine strings. The new string created is referred to as an object. To merge two strings into a single object, you may use the "+" operator.

